POSTS
Big PhD questions: Should I do a PhD?
by Luis P. Prieto, - 20 minutes read - 4241 wordsIf you are reading this, chances are that you have already decided to do a PhD. Yet, you may know someone who is considering a doctoral degree (or you may be offering such a position as a supervisor to prospective students). This post is for them. In this new type of post, we will look at big questions facing any PhD student. Today, we analyze the question that precedes all the other big PhD questions: “should I do a PhD?”. Below, I offer a couple of quick, simple ways to look at this important life decision, and a list of 10 factors to consider when offered (or seeking) a PhD position.
The other day, some researcher colleagues told me about a brilliant master student of theirs, to whom they were offering the possibility of doing a PhD in their lab. However, the student was doubtful: should she embark on this long and uncertain journey, on a low income, foregoing higher salaries (and maybe more stability) if she entered the job market right away? Her family and friends, not really knowing what a PhD or academia are like, were also giving all sorts of (sometimes contradictory) advice. Should she do a PhD?
This simple question is not asked nearly as much (or as seriously) as it should. Many people (myself included!) have embarked on this challenging, marathon-like experience without a clear idea of why it is the right choice for them, for that particular moment in their lives. Given this lack of clarity, we shouldn’t be surprised by the high rates of people that drop out of doctoral programs, or that develop mental health issues, once they hit the hard parts of the journey.
So, let’s approach this big PhD question from a few different angles…
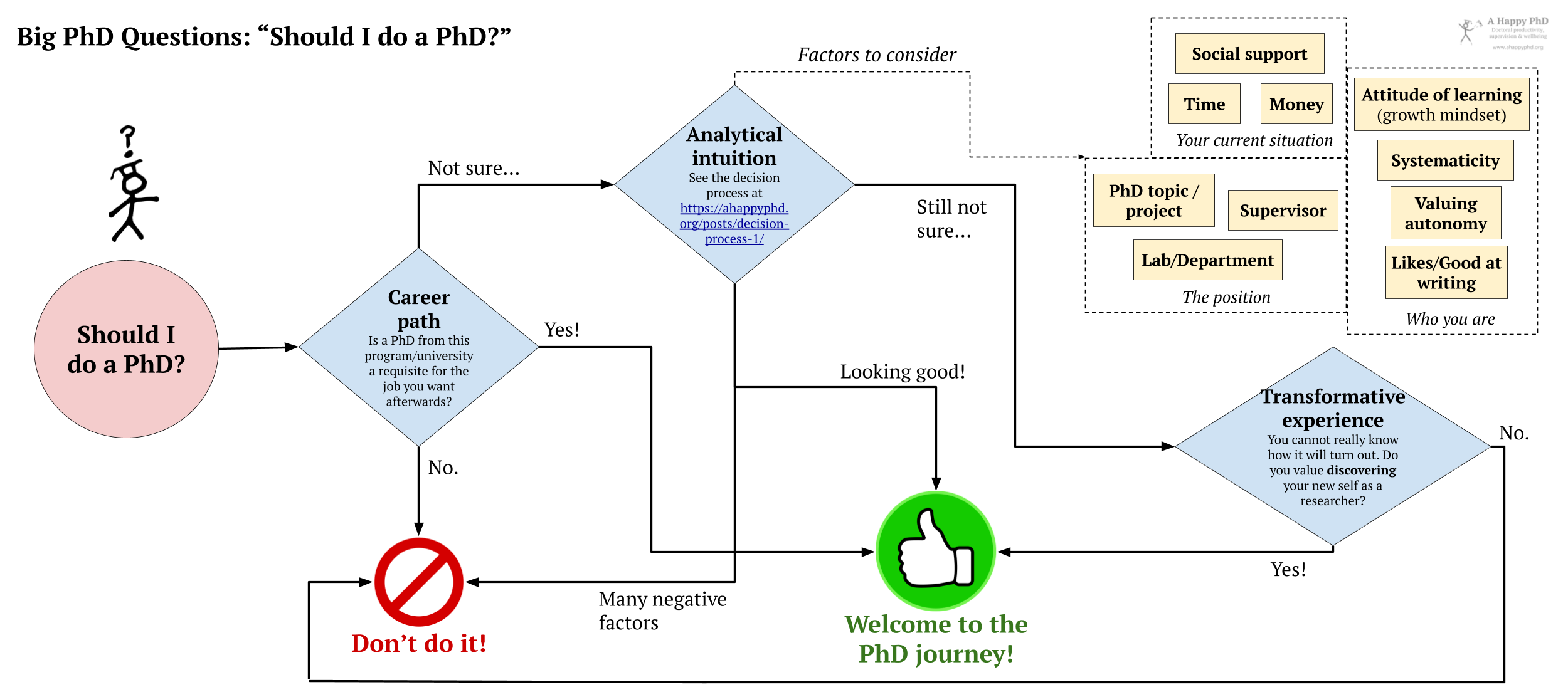
A first short answer: Thinking about the career path
When I started my PhD back in 2007, coming from a job in the industry, I only had a very nebulous idea that I might like to do research professionally (albeit, to be honest, what I liked most about research was the travelling and the working with foreign, smart people). My employer back then was encouraging us to earn doctoral degrees as a way to pump up the R&D output. Thus I started a PhD, without a clear idea of a topic, of who would be my supervisor, or what I would do with my life once I had the doctoral degree in my hands.
This is exactly what some career advice experts like Cal Newport say you should NOT do. They argue that graduate degrees (also including Master’s) should not be pursued due to a generic idea that having them will improve our “job prospects” or “hirability”, that it will help us “land a job” more easily. Rather, they propose to take a cold, hard look to what we want to do after the doctorate (do I want to be a Professor? if so, where? do I want a job in the industry? in which company? etc.). Then, pursue the PhD only if we have proof that a PhD, from the kind of university program we can get into1, is a necessary requisite for that job.
If you aspire to be an academic (and maybe get tenure), do not take that aspiration lightly: such positions are becoming increasingly rare and competition for them is fiercer than ever. Take a look at the latest academic positions in your field at your target university, and who filled them. Do you have a (more or less) similar profile? In some highly prestigious institutions, you need to be some kind of “superstar” student, coming from a particular kind of university, if you want to get that kind of job.
In general, I agree with Cal that we should not generically assume that a PhD will be useful or get us a job in a particular area, unless we have hard evidence on that (especially if we want a job in the industry!). Also, I agree that the opportunity cost of a PhD should not be underestimated: if you enroll in a PhD program, you will probably be in for a reduction in salary (compared with most industry jobs), for a period of four or more years!
Yet, for some of us, the plan about what to do after the PhD may not be so clear (as it was my case back in 2007). Also, being too single-minded about what our future career path should look like has its own problems2. Indeed, there are plenty of examples of people that started a PhD without a clear endgame in mind, who finished it happily and went on to become successful academics or researchers. Ask any researcher you know!
So, if this first answer to ‘should I do a PhD?' did not give us a clear answer, maybe we need a different approach. Read on.
A longer answer: Factors for a happy (or less sucky) PhD
If we are still unsure of whether doing a PhD is a good idea, we can do worse than to follow the decision-making advice I have proposed in a previous post for big decisions during the PhD. In those posts, I describe a three-step process in which we 1) expand our understanding of the options available (not just to do or not do a PhD, but also what PhD places are available, what are our non-PhD alternative paths, etc.); 2) analyze (and maybe prototype) and visualize the different options; and 3) take the decision and move on with it.
However, one obstacle we may face when applying that process to this particular decision is the “analytic intuition” step, in which we evaluate explicitly different aspects of each of the options, to inform our final, intuitive (i.e., “gut feeling”) decision. If we have never done a PhD or been in academia, we may be baffled about what are the most important aspects to consider when making such an evaluation about a particular PhD position, or whether a PhD is a good path for us at all.
Below, I outline ten factors that I have observed are related to better, happier (but not necessarily stress-free!) PhD processes and outcomes. Contrary to many other posts in this blog (where I focus on the factors that we have control over), most of the items below are factors outside our direct control as PhD students, or which are hard to change all by ourselves. Things like our current life situation, what kind of person we are, or the particular supervisor/lab/topic where we would do the PhD. Such external or hard-to-change aspects are often the ones that produce most frustration (and probably lead to bad mental health or dropout outcomes) once we are on the PhD journey:
- Time. This is pretty obvious, but often overlooked. Do we have time in our days to actually do a PhD (or can we make enough time by stopping other things we currently do)? PhD programs are calibrated to take 3-4 years to complete, working at least 8 hours a day. And the sheer amount of hours spent working on thesis materials seems to be the most noticeable predictor of everyday progress in the PhD, according to (still unpublished) studies we are doing of doctoral student diaries and self-tracking (and, let’s remember, progress itself is the most important factor in completing a PhD3). And there is also the issue of our mental energy: if we think that we can solve the kind of cognitively demanding tasks that a PhD entails, after 8 hours of an unrelated (and potentially stressful) day job, maybe we should think again. Abandon the idea that you can do a PhD (and actually enjoy it) while juggling two other day jobs and taking care of small kids. Paraphrasing one of my mentors, “a PhD is not a hobby”, it is a full-time job! Ignore this advice at your own risk.
- Money. This is related to the previous one (since time is money, as they say), but deserves independent evaluation. How are we going to support ourselves economically during the 3+ years that a PhD lasts? In many countries, there exist PhD positions that pay a salary (if we can get access to those). Is that salary high enough to support us (and maybe our family, depending on our situation) during those years? If we do not have access to these paid PhD positions (or the salary is too low for our needs), how will we be supported? Do we have enough savings to keep us going for the length of the PhD? can our spouse or our family support us? If we plan on taking/keeping an unrelated job for such economic support, read again point #1. Also, consider the obligations that a particular paid PhD position has: sometimes it requires us to work on a particular research project (which may or may not be related to our PhD topic), sometimes it requires us to teach at the university (which does not help us advance in our dissertation), etc. As stated in the decision process advice, it is important to talk to people currently in that kind of position or situation, to see how they actually spend their time (e.g., are they so stressed by the teaching load that they do not have time to advance in the dissertation?).
- Having social support (especially, outside academia). This one is also quite obvious, but bears mentioning anyways. Having strong social ties is one of the most important correlates of good mental health in the doctorate, and probably also helps us across the rough patches of the PhD journey towards completion. Having a supportive spouse, family, or close friends to whom we can turn when things are bad, or with whom we can go on holidays or simply unwind and disconnect from our PhD work from time to time, will be invaluable. Even having kids is associated with lower risk of mental health symptoms during the doctorate (which is somewhat counter-intuitive, and probably depends on whether you have access to childcare or not). A PhD can be a very lonely job sometimes, and there is plenty of research showing that loneliness is bad for our mental and physical health!
- An attitude of learning. Although this is a somewhat squishy factor, it is probably the first that came to my mind, stemming from my own (anecdotal, non-scientific) observation of PhD students in different labs and universities. Those that were excited to learn new things, to read the latest papers on a topic, to try a new methodology, seem to be more successful at doing the PhD (and look happier to me). People that are strong in curiosity seem a good match for a scientific career, which is in the end about answering questions (even if curiosity also has its downsides). This personal quality can also be related to Dweck’s growth mindset (the belief that our intelligence and talents are not fixed and can be learned)4. If you are curious, this mindset can be measured in a variety of ways.
- A knack for systematicity and concentration. This one is, in a sense, the counterweight to the previous one. Curious people often have shorter attention spans, so sometimes they (we, I should say) have trouble concentrating or focusing on the same thing for a long period of time. Yet, research is all about following a particular method in a systematic and consistent way, and often requires long periods of focus and concentration. Thus, if we find ourselves having trouble with staying with one task, idea or project for more than a few minutes in a row, we may be in for trouble. The PhD requires to pursue a single idea for years!
- Valuing autonomy. As I mentioned in passing above, a PhD is, by definition, an individual achievement (even if a lot of research today requires teamwork and collaboration). Thus, to be successful (and even enjoy) the process of the PhD, we have to be comfortable being and working alone, at least for some of the time. Spending years developing our own contribution to knowledge that no one else has come up with before, should not feel like a weird notion to us. Even if it occasionally comes with the uncomfortable uncertainty of not knowing whether our ideas will work out. In human values research they call this impulse to define our own direction, autonomy5, and many of my researcher friends tell me it is a very common trait in researchers. However, these values are very personal and very cultural. To evaluate this factor, we could simply ask ourselves how much we value this autonomy over other things in life, or use validated instruments to measure relative value importance, like the Portrait Values Questionnaire (PVQ).
- Liking and/or being good at writing. I have written quite a bit here about the importance (and difficulty) of writing in the PhD. Be it writing journal and conference papers, or the dissertation tome itself, every PhD student spends quite a bit of time writing, as a way of conveying new knowledge in a clear, concise and systematic way. Learning to write effectively is also known to be one of the common difficulties of many PhD processes6, due to reasons discussed elsewhere. Hence, if we hate writing, we should think carefully about spending the next 3+ years doing something that necessarily involves quite a bit of writing, other people spotting flaws in your writing, and rewriting your ideas multiple times. Please note that I don’t consider being a good (academic or nonfiction) writer a necessary requisite for a PhD, as it can be learned like any other skill (again, the learning attitude in point #4 will help with that!). But being good at it will certainly make things easier and will let you focus on the content of the research, rather than on learning this new, complex skill.
- Your supervisor(s). Rivers of ink have been spilled over how important the role of the supervisor(s) is for a successful PhD6,7. Although most doctoral programs have mechanisms for changing supervisors after the start of a doctorate, it is not an easy change and can significantly delay its finishing. The choice of PhD supervisor can thus be the target of its own decision process (if you can choose with whom to work for your dissertation). A non-exhaustive list of aspects I would evaluate in order to choose a supervisor includes:
- Compatibility (or, as they call it in the literature sometimes, the “fit”) of our and their personalities, ways of working (e.g., do they like micro-managing people, but you hate people looking over your shoulder?) and expectations about what a doctoral student and a supervisor should do.
- A concern for you as a person. Since this is difficult to evaluate as we may not know each other yet, we could use their concern about the people that work in their lab (beyond being just a source of cheap labor), as a proxy.
- Enthusiasm for the field of research or topic, its importance in the world, etc. A cynic, jaded researcher may not be the best person to guide us to be a great member of the scientific community.
- A supervisor that is well-known, an expert in the particular topic of the dissertation. Looking at the number of citations, e.g., in Google Scholar is a good initial indicator, but look at the publication titles (are they in similar topics to those they are offering you as your doctoral project? if not, that may mean that this person may also be new to your particular dissertation topic!).
- Related to the previous one, does this researcher have a good network of (international) contacts in other institutions? Do they frequently co-author papers with researchers in other labs/countries? We may be able to benefit from such contact network, and get wind of important opportunities during the dissertation and for our long-term research career.
- Openness (and time!) to talk about what the doctoral student job entails, potential barriers and difficulties, etc. This can be a proxy to both their general busyness (you will not get much guidance if they can never meet you because they have too little time) and their communication skills (something critical to consider when signing up to work closely with someone for years).
- Whether the supervisor is an ethical person. This is very important but seldom considered (maybe because it is hard to evaluate!). For sure, we don’t want to be backstabbed or exploited by our supervisor!
- Whether this person(s) is known to be a good supervisor. Have they already supervised other doctoral students to completion, in nominal time and with good grades? Do they regularly attend trainings and professional development about doctoral supervision? Do they seem to care about this part of their job for its own sake (rather than as a mere medium to get cheap labor)?
- You may be wondering how you are going to gather information about all the aspects mentioned above. Sometimes you can ask the supervisor directly, but you can also talk with current PhD students of this person, or students in the same lab/department (but do not take what they say at face value: partisanship, gossip or rivalries may be at work!). If you have the time and the opportunity, try to “prototype” (see the decision process post) the experience of working with this supervisor: do a master thesis with them, or a summer internship, or use the work on a joint PhD project proposal (a pre-requisite before being accepted as a doctoral student in some institutions). Some things we don’t know we like until we try them!
- Of course, all of the above are two-way streets. As prospective students, we also need to show to a potential supervisor that we are open to talk about expectations, that we are somewhat flexible, dependable, etc. Be very conscious of this in your interactions with supervisors and other people in their lab!
- The lab/department where you will do the dissertation. Again, there are many things to consider here. Is there an actual research group, or will we be doing our research in isolation with our supervisor? Normally, the former is preferable, since that gives us more resources to draw from if the supervisor is not available. Is the research group well known in the field (again, look at citations, invited talks, etc. of different group members)? But especially, try to get an idea of the lab’s working atmosphere: is it stressful, relaxed, collaborative, competitive…? As with the previous point, we could prototype it by spending some time working there, or we can interview one or more people working in the lab. If we do the latter, it is better to go beyond direct questions that will give vague (and maybe unreliable) answers, like “it’s good”. Rather, take a journalistic approach, and ask people to narrate concretely what the routines are in the lab, when and how did they last collaborate with another student, or the last conflict arising in the lab. Then, decide whether this kind of ambience is a good fit for you.
- The concrete PhD topic. We should find out (e.g., from our prospective supervisor) whether the topic of the dissertation is already well-defined, or rather we will have to explore and define it ourselves (both options have pros and cons, and again it depends whether we value more autonomy and exploration, or having a clear path ahead). Is the area or keywords of the PhD topic going up or down in popularity (see here for a potential way to find out)? Are there clear funding schemes that specifically target this kind of research topic, at the national or international level? How easy is it to collect evidence for this kind of research (empirical data is a critical element in almost all research fields, so we want easy and reliable access to them)? I would not evaluate a PhD topic on the basis of whether we love it right now, as we never know much about any research area when we start a doctorate (even if we think we do!). An attitude of learning and curiosity (see #4) will take care of that. Rather, talk with the supervisor about how the research process might look like, what kind of activities will take up most of our time (reading papers? doing labwork? interviewing people?): do we find those activities interesting?
Yet, after considering all these 10 factors separately, we may not be clear on the decision (maybe some aspects are good, others not so much). If, after all this thinking and gathering of information we still are not sure, there is one last idea I can offer…
One last answer: We cannot really know (the PhD as a transformative experience)
We could also frame the question of whether to do a PhD as what philosopher L.A. Paul calls a “transformative experience”8. Doing a PhD is a big life decision (like becoming a parent or taking a powerful drug) through which we probably will transform ourselves into another person, with different preferences and even different values.
I can think of many ways in which I am a different person now, due to the transformative experience of doing my PhD: I am now able to read and understand scientific papers (e.g., when I come across a new idea or “expert”, I go and read actual research papers about that), and I can evaluate the reliability of different types of evidence; I trust more scientific advances and consensus; I am more comfortable speaking (and writing) in English; I am more aware of culture and life in other countries, and I have less chauvinistic views of foreigners (due to my international experience gained as a researcher). Et cetera.
Paul’s argument regarding transformative experiences is that there are limitations to simulating (i.e., imagining) whether we will like the experience, as our own values and preferences may be changed by the very experience we try to simulate. For similar reasons, there are limits to the usefulness of asking others about the decision (and trusting their testimony), since they also have different values, preferences and coping strategies than us. Even looking at the latest and most reliable research on the topic (e.g., whether PhD students end up happier and/or more satisfied with their lives than people who did not take that choice) is of limited help, since such research (of which there is little!) often concentrates on average effects, and we may not be “average”.
What to do, then?
L.A. Paul’s way out of this dilemma seems to be a reframe of the question: "Will I be happier if I do a Ph?“, "Should I do a PhD?“. Rather, we can ask: “Do I value discovering my new self as a researcher/doctor?". In a sense, this new question targets a key intrinsic value we may (or may not) have: Do we appreciate learning, exploring, getting novel experiences, discovering and remaking ourselves (related to point #4 above)? If yes, a PhD might be a good idea. If we prefer stability, things (and our life) as they have always been, the status quo… maybe we will not appreciate this transformation that much.
There is no right or wrong answer. Only your answer.
The diagram below summarizes the main ideas in this post. Reflect upon these questions, and make your own choice. Take responsibility for your choice… but don’t blame yourself for the outcome, i.e., if it does not work out as you expected. There are too many inherent uncertainties about this decision that cannot be known until we actually walk the path.
Did these arguments and factors help you think through the decision of doing (or not doing) a PhD? What did you decide in the end and why? I’d be very curious to know… Let us know in the comments section below!
Header photo by Zeevveez
-
This seems especially important in the U.S. higher education and research market, which is quite clearly stratified, with research-focused and more teaching-focused universities, “Ivy Leagues”, etc. ↩︎
-
If we get obsessed with going a particular way and we fail to achieve it (or even if we achieve it and find out that it’s not what we thought it’d be), we may end up feeling stuck and/or depressed. See Burnett, W., & Evans, D. J. (2016). Designing your life: How to build a well-lived, joyful life, for ideas on how to get “unstuck” in those cases. ↩︎
-
De Clercq, M., Frenay, M., Azzi, A., Klein, O., & Galand, B. (2021). All you need is self-determination: Investigation of PhD students’ motivation profiles and their impact on the doctoral completion process. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 16, 189–209. ↩︎
-
Claro, S., Paunesku, D., & Dweck, C. S. (2016). Growth mindset tempers the effects of poverty on academic achievement. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(31), 8664–8668. ↩︎
-
Schwartz, S. H. (2012). An Overview of the Schwartz Theory of Basic Values. Online Readings in Psychology and Culture, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.9707/2307-0919.1116 ↩︎
-
Sverdlik, A., Hall, N. C., McAlpine, L., & Hubbard, K. (2018). The PhD experience: A review of the factors influencing doctoral students’ completion, achievement, and well-being. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 13, 361–388. https://doi.org/10.28945/4113 ↩︎
-
Masek, A., & Alias, M. (2020). A review of effective doctoral supervision: What is it and how can we achieve it? Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(6), 2493–2500. ↩︎
-
Paul, L. A. (2014). Transformative experience. OUP Oxford. ↩︎

Luis P. Prieto
Luis P. is a Ramón y Cajal research fellow at the University of Valladolid (Spain), investigating learning technologies, especially learning analytics. He is also an avid learner about doctoral education and supervision, and he's the main author at the A Happy PhD blog.